Portima Information Security Policy
Versie 1.4
Document summary | This document outlines Portima's commitment to protecting the confidentiality, integrity, availability, non-repudiation, and authentication of information (CIANA). The purpose of this policy is to ensure the protection of information assets and reduce the risk of information security incidents. | ||
Intended Audience | Portima employees, contractors and any other individuals who access Portima's systems and data. | ||
Process | Information Security | ||
Issue date | 05/06/2025 | ||
Next review date | 05/06/2026 | ||
Document manager | Portima ISMS Coordinator | ||
Approval level | CODIR | ||
Classification level | Public | ||
Reference | ISMS 001 POL | ||
Version | V.1.4 | ||
Status | Approved | Date | 05/06/2025 |
The latest approved version of this document is available at: |
Sharepoint and portima.com |
History
Version | Updated by | Date | Description of changes |
| 1.0 | 09/08/2023 | First approved version | |
1.1 | ISMS Coordinator | 24/08/2023 | Classification level adapted from internal to public Audience for Data Privacy Policy |
| 1.2 | ISMS Coordinator | 25/01/2024 | Roles and responsibilities |
| 1.3 | ISMS Coordinator | 23/01/2025 | Included DORA related requirements |
| 1.4 | ISMS Coordinator | 05/06/2025 | Adding AI Policy in the ISP framework |
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Scope
- Portima’s commitment to information security
- Information security policy framework
- 4.1 Network Protection Policy
- 4.2 Cryptographic Control Policy
- 4.3 Third Party Security Policy
- 4.4 Physical and Environmental Security Policy
- 4.5 Incident Management Policy
- 4.6 Business Continuity Management Plan
- 4.7 Secure Development Policy
- Information Security Risk Management
- Information security roles and responsibilities
- Data Classification
- Training and Awareness
- Review and Auditing
- Policy enforcement
- Reference
- Glossary
1. Introduction
This policy outlines Portima's commitment to protecting the confidentiality, integrity, availability, non-repudiation, and authentication of information. The purpose of this policy is to ensure the protection of information assets and reduce the risk of information security incidents.
The information security policy describes Portima’s responsibility to:
- Protect the confidentiality, integrity, availability, non-repudiation, and authentication of business-critical information, based on good practices;
- Ensure that the aforementioned information is exchanged with external parties (e.g., stakeholders, customers and/or suppliers) in a secure manner;
- Prevent or minimizing the impact of information security incidents or breaches.
- Protect Portima’s business, reputation and to safeguard our people; and
- Ensure that Portima’s employees understand their roles and responsibilities.
It also defines procedures, baselines, and practices for the aforementioned resources to acquire adequate knowledge of the security policy and how to protect information from unauthorised use or disclosure.
2. Scope
This policy applies to all employees, contractors, and any other individuals who access Portima's systems and data. It’s considered as an umbrella above other policies (see section 4).
This policy covers all information assets, including physical, electronic, and confidential information, stored in any format or location. Either these information assets are owned or controlled by Portima, including but not limited to:
- Cloud infrastructure;
- All servers, workstations, laptops, mobile devices, and other computing devices;
- All network infrastructure, including routers, switches, and firewalls; and
All data stored on Portima's systems, including but not limited to: financial information, personal information, confidential business information, and intellectual property.
3. Portima's commitment to information security
Portima’s CODIR acknowledges the expectations of both internal and external stakeholders regarding the information security posture of the organisation. More specifically, Portima’s CODIR is committed to achieve the following objectives:
- Protect the business processes and infrastructure related to software development, deployment and support of Brio and Portima Connect.
- Safeguarding the confidentiality, integrity, availability, non-repudiation, and authentication of its data, using a risk-based approach.
- Complying with the legal requirements and meeting its business partners’ expectations.
In order to support this commitment and achieve the information security objectives Portima established and operates an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This ISMS is comprised of information security policies, standards and procedures designed to maintain, review and continually improve information security across Portima from a risk-based perspective.
4. Information security policy framework
As part of the risk-based ISMS, Portima established an information security policy framework comprised out of information security policies outlining the information security requirements to be adhered to by Portima employees and contractors. This information security policy framework is subject to the ISMS’ continual improvement process ensuring that these policies are maintained, reviewed and updated when relevant.
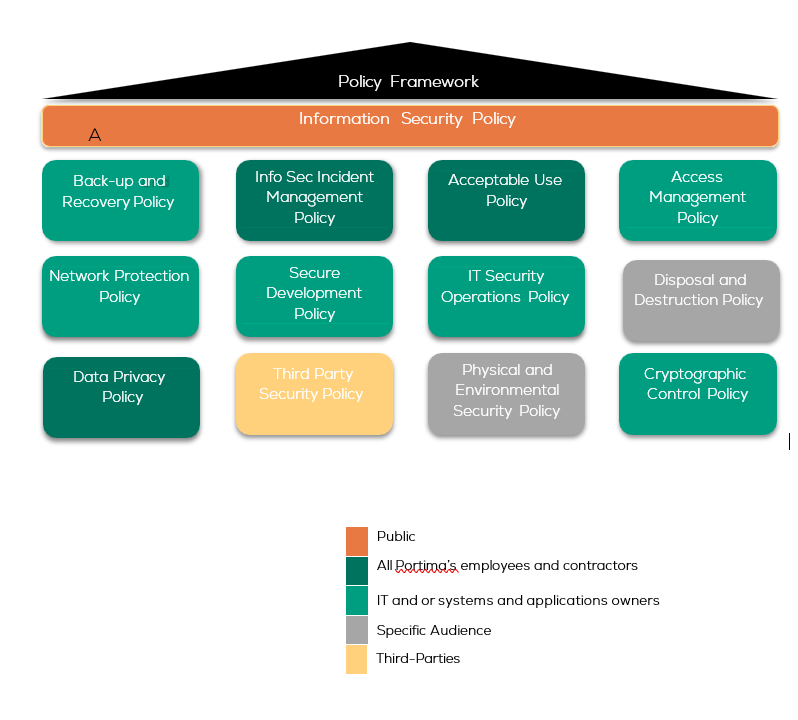
4.1 Network Protection Policy
Portima defined, formalized, and implemented a comprehensive Network Security policy to protect Portima’s information systems and data from unauthorized access and potential threats. This policy outlines guidelines for network usage, define authorized users, enforce secure remote access with strong authentication, assesses potential risks, and establishes protective measures to prevent misuse. Portima ensures that the Network Security Policy is regularly reviewed and updated to address evolving threats and technology changes, maintaining a high standard of network security across the organization. (DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554 - Art. 15)
4.2 Cryptographic Control Policy
Portima defined, formalized, and implemented a comprehensive cryptographic controls policy to ensure the proper and effective use of encryption for protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of sensitive information assets (in compliance with applicable regulation GDPR and DORA). Portima monitors adherence to these cryptographic controls and conduct regular audits to ensure compliance with this policy. (DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554 - Art. 15)
4.3 Third Party Security Policy
Portima defined, formalized, and implemented a comprehensive ICT Third-Party Security Policy. This policy outlines the security requirements and standards that all third-party ICT service providers must adhere to when accessing, processing, or managing Portima’s data and systems. The policy includes criteria for assessing, monitoring, and managing third-party security risks to ensure that these providers meet Portima’s security standards and effectively mitigate any associated risks. Portima regularly reviews and updates the ICT Third-Party Security Policy to ensure it remains aligned with evolving threats and regulatory requirements. (DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554 - Art. 15)
4.4 Physical and Environmental Security Policy
Portima defined, formalized, and implemented a robust Physical and Environmental Security Policy. This policy addresses the controls and procedures necessary to protect physical locations, prevent unauthorized access, and mitigate environmental risks. A visitor management procedure is documented. Clear desk requirements are adopted to ensure that classified information is securely stored and not accessible to unauthorized individuals. Portima regularly reviews and updates the Physical and Environmental Security Policy to adapt to emerging threats and ensure ongoing protection of its facilities and assets. (DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554 - Art. 15)
4.5 Incident Management Policy
Portima defined, formalized, and implemented an ICT incident management policy to effectively manage and respond to ICT incidents. This policy outlines a structured approach for identifying, reporting, investigating and remediating incidents to minimize the impact on operations, protect data, and prevent recurrence. The policy includes the requirement that any unauthorized access, modification, disclosure, or destruction of personal data, shall be reported immediately via the dedicated communication channels. undergo Additionally, it formalizes roles and responsibilities related to regarding communication and management of ICT incidents, ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of their duties in incident detection, response, and reporting. (DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554 - Art. 15)
4.6 Business Continuity Management Plan
Portima defined, formalized, and implemented a business continuity plan to restore critical functions, services, processes, and resources in the event of a major incident, crisis, or disaster, all within the defined and agreed-upon service levels. Portima regularly reviews and updates the Business Continuity Management Plan. During any business continuity event, Portima will maintain the same security standards as during normal operations, ensuring ongoing protection and resilience. (DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554 - Art. 11)
4.7 Secure Development Policy
Portima developed, documented, and implemented a comprehensive policy for the acquisition, development, and maintenance of Portima's ICT systems to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, availability, non-repudiation and authentication of data. This policy identifies security practices and methodologies, specifies technical requirements with a focus on ICT security, and defines measures to mitigate risks of alterations or manipulations. A documented policy outlines requirements for testing and approving ICT systems, including source code reviews and security testing before deployment. Only anonymized, pseudonymized, or randomized data are used in non-production environments to protect data integrity and confidentiality. Controls are implemented to secure in-house or third-party-developed source codes, and proprietary software are analyzed before production deployment. The policy also covers ICT systems managed by users outside the ICT function, using a risk-based approach.
5. Information Security Risk Management
The Chief information security officer shall ensure that a risk assessment is conducted at least annually or when significant changes occur to Portima’s organisation or IT environment. This risk assessment shall be conducted in line with Portima’s Risk Assessment Methodology. The assessment shall provide a comprehensive explanation of the information security risks currently faced by Portima and determine specific treatment actions to manage these risks.
6. Information Security roles and responsabilities
Information security roles and responsibilities are defined and assigned at the different levels of Portima’s organisation while ensuring the segregation of duties. These roles and responsibilities are outlined and documented as part of the organisation’s ISMS Manual.
Role | Description | Name |
CEO |
| Jan Peeters |
Chief Information Officer (CIO) |
| Christophe Cloesen (CIO) |
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) |
| Mohamed Amine Youssef |
ISMS Coordinator |
tracked within the ISMS.
| Valérie Dechamps |
System owner |
| Cécile Louvrier (Director Portima Connect) Christophe Cloesen |
Data Protection Officer (DPO) |
| Valérie Dechamps |
Chapter lead Product Owner |
| Julien Rolland (PC) Matthieu Legros (PC) Daniel Wuidart (Brio) Koen Ramakers (Brio) Bart Pollet (Infra) Christophe Arnould (BCC) John Croon (Facility Mgr) |
Risk Officer |
| Caline Villacres |
Product security champion |
| Mohamed Amine Youssef |
7. Data Classification
All Portima’s employees should classify and handle information based on Portima classification scheme outlined below:
Classification Levels | Description |
Confidential | Confidential data is information available only for authorised users who really need access to the information (e.g., strategic information, broker client data). |
Internal use | By default, all documents and data belonging to Portima are considered “internal use”, except if they are classified “public” or “confidential” |
Public | Public data is information that everyone has access to. It’s public information, freely accessible and can thus be openly used, reused and shared. |
8. Training and Awareness
Portima shall provide regular information security training and awareness activities (eg: phishing campaigns) to raise resources having access to its systems and data awareness regarding information security.
During onboarding, the employee/contractor shall also attend awareness sessions on the following topics:
- General ICT Security awareness
- GDPR, DORA
- Phishing reporting
- Human firewall
All those trainings and security awareness activities are mandatory.
9. Review and Auditing
[1] Portima shall review and audit in a yearly basis its security policies and practices to ensure that they are effective, up-to-date and reflect changes in technology, business processes, and regulatory requirements.
[2] The Information Security Management System (ISMS) shall be audited at least once a year, with the results shared with the financial client upon request, in accordance with Regulation (EU) 2022/2554, Art. 6, par. 5. This audit will incorporate an annual ICT internal audit plan, which shall be defined, formalized, and periodically reviewed to ensure ongoing effectiveness, as required by Regulation (EU) 2022/2554, Art. 6, par. 6.
[3] ICT audits shall be conducted by independent internal auditors with the necessary knowledge and skills to assess ICT risks effectively, as per Regulation (EU) 2022/2554, Art. 6, par. 6.
[4] The frequency and focus of ICT audits shall be guided by identified ICT risks, ensuring higher-risk areas receive appropriate attention, in line with Regulation (EU) 2022/2554, Art. 6, par. 6.
[5] A defined and formalized process shall be in place to monitor remediation actions for critical ICT audit findings, ensuring timely resolution and compliance with Regulation (EU) 2022/2554, Art. 6, par. 7
10. Policy enforcement
The policy statements containing the terms “shall” and “shall not” indicate a requirement, while the terms “should” and “should not” indicate a recommendation.
Violation of this information security policy or any of Portima security policies or security procedures, whether through negligence or with malicious intent might be subject to administrative discipline and possible criminal pursuit.
11. Reference
ISO 27001:2022 Controls (Annex A) |
5. Leadership |
6. Planning |
A.5.1 Policies for information security |
A.5.2 Information security roles and responsibilities |
A.5.12 Classification of information |
A.5.13 Labelling of information |
A.5.24 Information security incident management planning and preparation |
| DORA Regulation |
| DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554 - Art.6, 11, 14, 15 |
| DORA JC_2023_86_ Final_report_on_draft_RTS_on_ICT_Risk_Management_Framework |
12. Glossary
Term | Description |
Availability | A principle of assuring that information is accessible to and usable by an authorised individual or entity when required. |
Confidentiality | Preserving authorized access to ensure that information and systems are only accessible to authorised users. |
Integrity | The guarding against improper information modification or destruction. |
Information | Knowledge concerning objects, such as facts, events, things, processes, or ideas that, within a certain context, has a particular meaning. |
Information security | The set of the administrative and the technical measures (practices and methods) taken to ensure the protection of the Portima’s information and information systems. |
| Information security incident | A single or a series of unwanted or unexpected cyber security events that are likely to compromise organisational activities. |
| ICT incident | ICT-related incident means a single event or a series of linked events unplanned that compromises the security of the network and information systems, and have an adverse impact on the availability, authenticity, integrity or confidentiality of data, or on the services provided by the entity |
| Risk | The degree of danger that a threat might materialise if one or more vulnerabilities in an information system were to be exploited. |
| ISMS | A management system comprised of information security policies, roles and responsibilities to structurally identify and manage cyber risks while creating visibility on Portima’s information security posture. |
| Network security | The protection of a computer network and its resources from unauthorized access, misuse, or damage, ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and availability |
| Authorization | The process of granting or denying access to specific resources or actions within a system based on assigned permissions. |
| Authentication | The verification of the identity of a user, device, or program before allowing access to a system or its resources. |
| Non-Repudiation | The assurance that a party cannot deny the authenticity of their signature or the validity of a transaction, providing proof of the origin and integrity of the data involved. |
| Cryptography | The practice of securing information by converting it into an unreadable format to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Encryption | The process of encoding information into a secure format that can only be decoded by authorized entities. |
| Third-party security | The protection of an organization’s data and systems when accessed or managed by external service providers or vendors. |
| Physical and Environmental Security | The protecting of an organization’s physical assets from threats such as unauthorized access, theft, or natural disasters. |
| Business Continuity | The planning and processes to ensure that critical functions and services can continue during and after a major disruption. |
| Cyber resilience | The ability of an organization to withstand, respond to, and recover from cyberattacks or other disruptions to its digital operations. |